Each person's hair has different natural pigments. Colorists use the Oswald circle to achieve the desired color when coloring and follow the basic rules for mixing colors to correct natural and artificial tones.
Basic concepts of color
The global science of colors is called color science. She studies them in conjunction with psychology, physics, history and aesthetics. Color science presents colors as a phenomenon of culture and sociality.
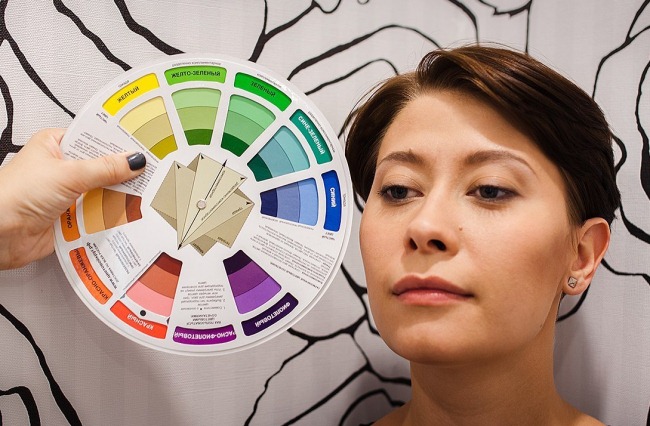

Coloristics is one of the departments of color science that studies colors more deeply, touching on the theory of its perception and application in different spheres of life. Coloring in hairdressing is a technique and rules for mixing colors.
Its basic concepts include:
| Term | Description |
| Color tone | The main parameter of any color, which describes which part of the spectrum it belongs to. |
| Chromaticity | The property determines the quality and purity of the color. It is an indicator of the presence of gray, white or black blotches in the base color. Almost all colors are chromatic, but with varying degrees of severity. |
| Achromaticity | A property expressing colorlessness. Achromatic colors include colors that do not split the light beam into separate, that is, rainbow colors: white, black and gray. |
| Lightness | The degree to which the selected color differs from white. |
| Saturation | This parameter determines the depth and intensity of the color in relation to the gray. On the spectrum, more saturated colors are located farther from gray, while less saturated colors are closer. |
| Brightness | This parameter determines the total amount of white light in each color. On the spectrum, brighter colors are closer to white, and less bright ones are farther away. |
| Shade | This is the color to which white was added. In the spectrum, red is the main color, and pale red is already a hue-color. |
| Shadow | This is the color black was added to. In the spectrum, red is the main color, and dark red is already a hue-color. |
| Key | This is the color that gray has been added to. Each addition of gray changes the key by exactly 1 gradation. |
| Subtone | This is an admixture of other colors to the base paint. |
Features of the choice of colors by color types of appearance
Coloristics allows you to accurately mix colors to obtain the desired color and correctly select it for the color type of a person.
The color wheel, the combination of colors of which is carried out according to certain rules, allows you to create cold and warm shades and tones. Warm colors include all colors that can turn into orange, that is, have a yellow or golden undertone. Cold colors include all colors that gradually turn into purple, that is, they have a blue undertone.
There are 4 color types of appearance, each of which is suitable for a certain hair coloring:
| Color type | Features: | Suitable colors for hair coloring |
| Spring |
|
|
| Summer |
|
|
| Winter |
|
|
| Fall |
|
|
The recommended colors can be adjusted as desired, but you must adhere to natural hue, lightness, and saturation.
3 primary colors in colouristic and their combination
Coloristics distinguishes 3 primary colors:
- blue;
- red;
- yellow.
They form the natural hair color, and also correct their shade during coloring:
- Blue. It is the coldest and deepest. When painted, it is used to create shadow. This pigment is predominant in dark hair.
- Yellow. It is the warmest and most basic in blonde hair and blondes. When colored, adding it increases the lightness and brightness of the color.
- Red. In natural hair, this color creates a medium undertone and is used in combination with blue in a 1: 1 ratio.
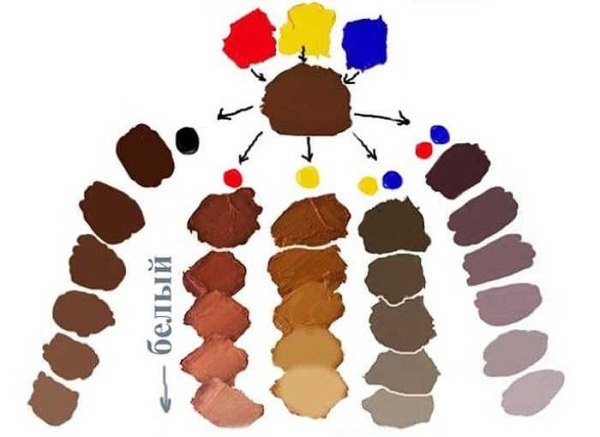
The color wheel, whose color combination creates additional colors, contains only color tones. To give the hair color saturation, lightness or brightness, additional pigments must be mixed into the base. Mixing the 3 primary colors produces a gray color. Depending on the concentration of pigments, lightness and saturation change.
Color mixing rules for hairdressers
Colorists and hairdressers must follow certain rules for preparing for dyeing and mixing colors:
- When mixing, use plastic, ceramic or glassware. It is strictly forbidden to dilute paints in a metal container.
- It is necessary to strictly observe the calculated proportions of the ingredients and the holding time of the resulting composition on the hair.
- It is forbidden to mix paints from different companies. All formulations must be identical and differ only in the series in the line of products.
- It is not recommended to mix more than 3 dyes with insufficient experience of the master.
- Pigments cannot be used in one composition: green-red, blue-orange, yellow-violet.
Color circle, the color combination of which is also governed by some rules, use immediately before mixing:
- Colors facing each other can neutralize each other.
- Only neutralize cold colors using warm ones.
- Warm colors that are one behind the other clockwise can be combined.
- Cool colors that are one behind the other counterclockwise cannot be combined.
- It is impossible to mix warm shades with cold ones at once.
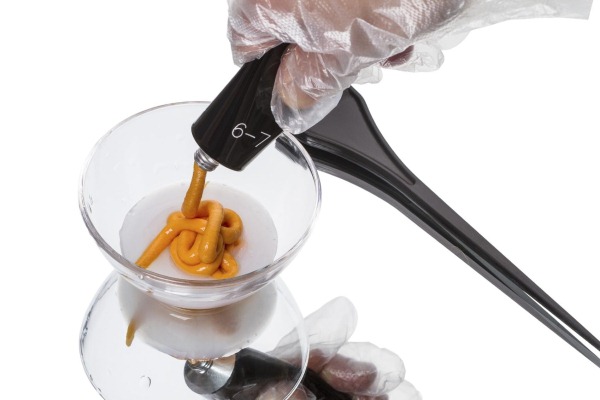
In what proportions to mix paints?
When mixing pigments, the desired hair color must be taken into account. They can be taken in the same quantity or by increasing the proportion of one of the paints.
Particular attention must be paid to the activator, or paint oxidizer. It contains hydrogen peroxide in various concentrations: from 1 to 12. The choice of activator depends on the hair structure, natural tone and color depth. The lower the percentage of peroxide, the less discoloration the oxidizing agent has.
| Peroxide concentration,% | Appointment |
| 1.2 to 1.9 | Dyeing in a tone close to natural. Darkening the tone. |
| 2.7 to 3.0 | Washing out the natural color by 1 tone. |
| 6 | Natural color washout in 2 tones. |
| 9 | Natural color washout in 3 tones. Suitable for dark and gray hair. |
| 12 | Natural color washout up to 7 tones. |
The paint must be taken depending on the length of the hair:
- 60 ml for short curls;
- 120 ml for medium curls;
- 180 ml for long curls.
It is recommended to mix the ingredients according to the standard scheme:
| Coloration | Color ratio (paint: oxidizer) |
| Persistent | 1:1 (3 %) |
| Tinting | 1: 2 (2% peroxide) |
| Painting gray hair | 1: 1 (from 9%) |
| Lightening | 1:2 |
| Staining with pastel pigments | 1:2 (1,2 %) |
| Staining with red pigments | 1: 1 (from 6%) |
| Highlighting | 1: 1.5 at 2 h of exposure 1: 2 at 1 hour exposure |
| Coloring | 1:5 (3 %) |
| Balayage and ombre | 1: 1, varies with saturation and lightness. |
The exposure time is calculated by the formula: volume of the activator + 15 min.
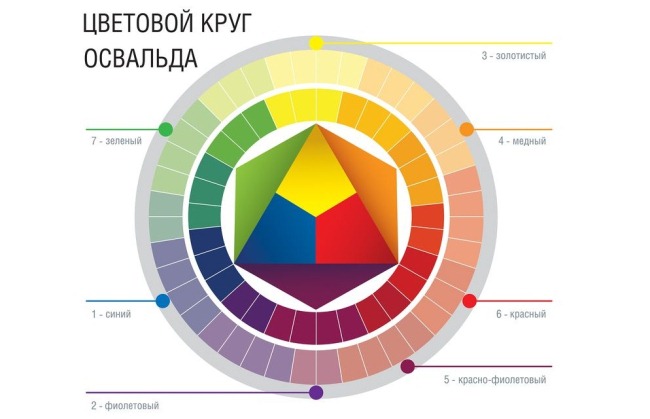
Color theory W. Oswald
According to Oswald's theory, white light is decomposed into a certain variety of colors, which he presented in the form of two cones connected by bases. The sharp ends of these figures represent achromatic colors before decay: black and white.
The base circumference is represented by rich colors of the spectrum from red to violet. The color wheel was created for colouristic use, like Oswald's simplified scheme. The combination of colors in it and the transitions into each other depend on the segments dividing the circle into 3 parts.
Each of them contains the main dyes: yellow, red and blue. Within each segment there are intermediate colors that are related to each other. Colors from adjacent parts of the circle are considered to be related-contrasting.
How to work with Oswald's color wheel
Oswald's circle is an auxiliary tool for painting.
It must be applied using several rules:
- To increase the saturation of the tone, a color located in the same segment is selected from the circle.
- To change the tone, shade or shadow, you need to combine 2 related contrasting colors.
- To neutralize unwanted reflections or shades, the color is taken from the end of the diagonal of the circle drawn from the already taken color.
It is worth remembering that the ideal combination of related-contrasting colors is obtained by mixing the same amount of the main and contrasting shade.
Primary colors
Primary colors are fundamental: they are not mixed with other colors. When mixed in an amount of 1: 1: 1, achromatic colors are obtained.
The blue pigment is considered dominant. Adding it to the coloring composition makes the curls dark and saturated. Red is a medium strength pigment. When added to blue, it makes the curls lighter, to yellow - darker. Yellow is the weakest pigment. When added to paint, it enhances the brightness and lightness of the color.
On the curls after discoloration, the primary colors give intermediate: blue, pink and light yellow.
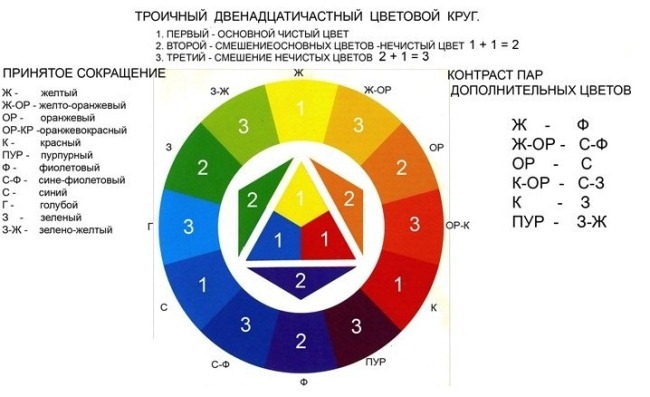
Secondary colors
These colors are obtained by mixing the primary ones:
- Blue and yellow form a green dye.
- Blue and red form a violet dye.
- Yellow and red form an orange dye.
They form an achromatic row when combined in the same amount. Secondary pigments are required to adjust the tone of the curls.
Tertiary colors
They are formed when primary and secondary pigments are combined into one composition. This method neutralizes unwanted undertones of the strands. They are also often used for color highlighting and coloring, as well as for adjusting the shade or shade of hair.
Harmonious colors
Pigments are considered harmonious if they are selected using the color wheel according to several principles:
- 2 colors are matched:
- using the diagonal of the circle passing through its center;
- from one segment.
- 3 colors are matched:
- On the principle of an equilateral triangle inscribed in the Oswald circle, its vertices are harmonious colors for mixing.
- On the principle of a right-angled triangle, the vertices of which are harmonious colors. The hypotenuse of the triangle must be the diameter of the circle.
- 4 colors are matched:
- By the principle of a rectangle inscribed in Oswald's circle;
- By the principle of a square inscribed in a circle.
- One segment principle.
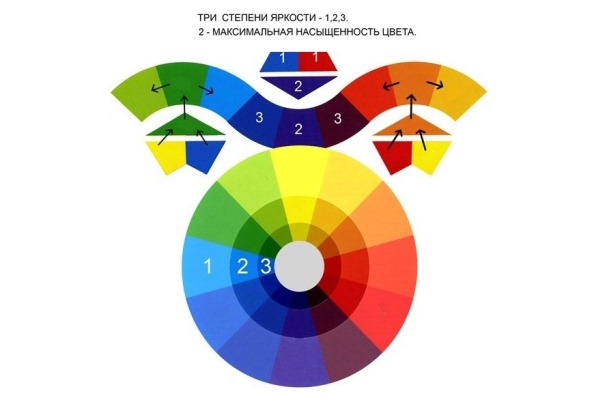
Monochrome colors
Monochrome are colors of the same gamut that have different levels of lightness and intensity.
The tints and shadows produced by combining the monochrome series are necessary for minor color correction of highlights and base tone.
Achromatic colors
White, black and gray colors are formed by mixing the primary pigments in different quantities. Achromatic range is used for highlighting or giving the hair a graying effect.
Ash shades
Such shades are difficult to obtain due to the content of yellow pigment in the hair. To give them a gray-pearl undertone, the colorist uses a method of neutralizing color using counter flowers.
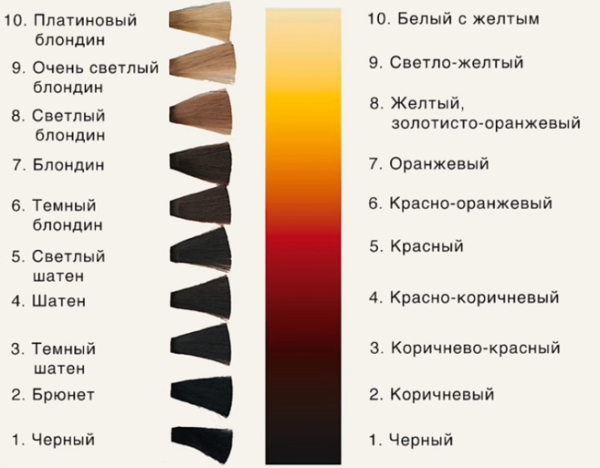
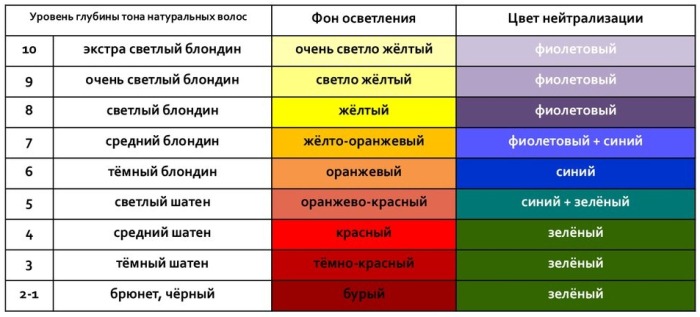
Depth tone level
Depth is the natural hair color prior to coloring. This concept is used in the shade combination table. It is determined visually by comparing a thick strand at the roots with a sample.
The number corresponding to the closer to natural color is the depth of the main tone. The division into tones is carried out from 1 to 10, that is, from the darkest to the lightest.
Lightening background and its neutralization
This concept shows the concentration of melanin in the curl shaft after the blue pigment has been displaced by an oxidizing agent. The remaining amount of red and yellow dyes indicates the background lightening. On coloring agents, this indicator is indicated by the second figure.
Each lightening background is specific to a specific depth:
| Saturation tone | Lightening background |
| 1 | Background: dark red to red. To neutralize it, you need to use a green pigment. |
| 3 | |
| 4 | |
| 5 | Orange background. Depth levels 5 and 7 have a double background: 5 - red-orange. Neutralization with blue-green pigment. 7 - orange-yellow. Neutralization with blue violet pigment. |
| 6 | |
| 7 | |
| 8 | Background: yellow. To neutralize it, you need to use a purple pigment. |
| 9 | |
| 10 |
The lighting background makes it possible to:
- correct and remove unwanted reflections and shades in time;
- increase color saturation and depth;
- increase the degree of lightness of the hair.
Basic color techniques
The color wheel, whose color combination is used not only by hairdressers, has a simplified color combination table. It is developed based on Oswald's theory especially for colorists.
Professional dyes have a specific sequence and color designation. The first number on the package is the level of tone depth: from 10 to 1. The second designation indicates the presence of auxiliary pigments, each digit in the number is taken into account:
| Designation | Tone or shade | Pigment |
| 1 | Natural | Green or light green |
| 2 | Ash | Light purple and violet |
| 3 | Gold | Yellow-red |
| 4 | Copper | Redhead |
| 5 | Red | Red |
| 6 | Violet | Blue violet |
| 7 | Terracotta | Red brown |
| 8 | Pale pearl mattifying | Blue |
Pigment combination table:
| Tone | Natural | Ashen | Golden | Copper | Red | Violet | Brown | Pearl |
| Depth of tone | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 10 | Light coloured | Light gray | Light gold | Light orange-chewed | — | — | — | Platinum |
| 9 | Blond | Ashen | Gold | Red yellow | Pink | Platinum | Kara-stranded | Bright pearl |
| 8 | Light blond | Light ash-flax-blond | Ash-blonde | Light red-yellow Blond | — | Rosewood of different intensities | — | Pearl |
| 7 | Blond | Ash-blonde | Ash-brown | Red yellow | Light red | — | Walnut | Scandinavian Blond |
| 6 | Dark blond | Dark ash-blond | Dark golden blond | Dark red yellow | Saturated red or pomegranate | Dark violet-tovoy-blond | Red-brown-brown | — |
| 5 | Light chestnut-new | Light ash | Light ash-like | Light red-yellow | Red fiery | Burgu-nd | Chocolate Brown | — |
| 4 | Chestnut | Ash gray | Gold | Red yellow | Dark red | Mahogany | Palisan-wood | — |
| 3 | Dark chestnut | Dark ash Gray | Dark gold | Dark red yellow | Ruby | Dark violet | Mocha Coffee with milk | — |
| 2 | Dark brown | — | — | — | — | Baklazha-new | — | — |
| 1 | The black | Glitter blue | Sparkle gold | Shine red-brown | Glitter red | Shine violet | Shine brown | — |
| Mick-moan | — | Blue gray | Gold | Copper Garnet | Scarlet | Violet | Green | Light coloured |
When using a table:
- pick up a natural tone;
- determine its intensity and depth;
- choose adjacent tones;
- knead paints.
The table allows you to determine what pigment can remain on the curls after dyeing.
Ombre
The ombre technique allows you to get a smooth transition from very dark paint to light. The range of pigments is selected depending on the client's color type. When performing the ombre technique, the main color and additional dyes are taken: lighter and darker than the base color.
Blonding
This technique differs from ombre by uniformly applying coloring compositions with different shades of blond to the strand. This technique is suitable for women with hair no darker than light brown.
Highlighting
Highlights are suitable for all women. The technique is based on lightening only some strands. Their number can vary up to 60% of the total curls. After dyeing, you need to inspect the strands and correct unwanted shades using the color wheel.
Hair dye compositions
Almost any hair coloring product contains:
- Alkaline compounds: ammonia or monoethanolamine; these are required to create a high pH environment. This loosens the top layers of the hair shaft and enhances the oxidation of the dye. Both substances are harmful by inhalation.
- Base. It is necessary to: soften the action of irritating agents on the scalp; creating a comfortable consistency for application; moisturizing hair.
- Hydrogen peroxide. This substance is a strong oxidizing agent. It is necessary to activate the oxidation processes of dyes and prepare the cuticle for staining. By the mechanism of action, peroxide is similar to ammonia.
- Oxidation pigments. They come in the form of aromatic amines, aminophenols or oxobenzenes. When interacting with an oxidizing agent, they turn into a stable colored substance.
Brightening agents
These funds are needed only to remove natural pigment from curls, therefore, the composition most often contains only a base and hydrogen peroxide. Phosphoric acid is used to soften the effect of peroxide. Depending on the desired degree of lightening, paints have different peroxide content.
Permanent
This category of coloring agents is the most aggressive in terms of impact on hair. Permanent paints displace natural pigment from curls as much as possible using ammonia or its substitutes.Such products, as a rule, consist of a coloring mass and an activator.
The composition includes:
- stabilizers for coloring compounds;
- shade-correcting additives;
- surfactants;
- caring components for hair restoration.
Semi-permanent paints
Such funds differ from permanent ones in less aggressive effects. They contain less peroxide and do not have alkaline compounds, so they do not change the natural tone of the curls. Such paints are washed off faster than permanent ones.
Tint products
Hair tint products are safe for the health of curls. They do not contain ammonia and hydrogen peroxide.
The composition of the products contains only ready-made oxidized dyes, so they do not stick into the hair structure and are washed off very quickly. They are used to add freshness and shine to an existing tone or a new shade.
Using the Oswald color wheel allows you to get the desired color even for novice hairdressers, and for experienced craftsmen - original hair coloring. You should not mix the coloring compositions yourself, it is better to seek help from a professional colorist who will help you choose the desired shade, eliminating the adverse effects of hair coloring.
Color basics video
How to start learning color and becoming a good colorist:





Good afternoon. This article says that mixing the three primary colors produces a gray color, but the figure clearly shows brown. Where is the mistake?